Powdery mildew is one of the most common plant diseases gardeners encounter. This fungal infection can affect a wide variety of plants, from flowers and vegetables to shrubs and trees. Left untreated, it can weaken your plants, reduce yields, and make your garden look less vibrant. The good news? With proper garden care and timely powdery mildew treatment, you can control and prevent this pesky fungus.
What is Powdery Mildew?
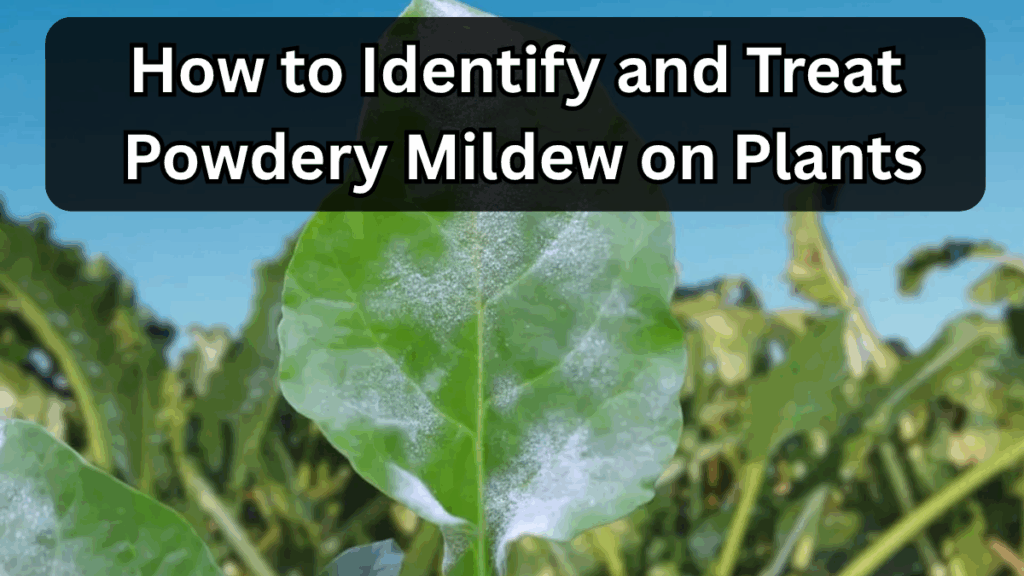
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that appears as a white or gray powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and buds of plants. It thrives in warm, dry climates and can spread quickly if not addressed.
Signs of Powdery Mildew
-
White or gray powdery spots on leaves, stems, or buds
-
Leaves curling, yellowing, or becoming distorted
-
Stunted plant growth
-
Premature leaf drop in severe cases
Common Plants Affected
| Plant Type | Symptoms Observed | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Roses | White powder on leaves and buds | Medium |
| Cucumbers & Squash | Yellowing leaves with white powder | High |
| Grapes | Powdery coating on young shoots | High |
| Zinnias & Phlox | White, powdery spots on leaves | Medium |
| Tomatoes | Leaf curling and powdery coating | High |
How to Identify Powdery Mildew
Identifying powdery mildew early is crucial for effective treatment. Look for:
-
Powdery coating: Starts as small white spots on leaves, gradually spreading.
-
Leaf distortion: Infected leaves may curl or become brittle.
-
Slow growth: Plants may show stunted growth and reduced flowering or fruiting.
-
Spreading pattern: Usually begins on older leaves but can move to new growth.
Effective Powdery Mildew Treatment
Managing powdery mildew requires a combination of prevention and treatment strategies. Here’s what works best:
Pruning and Removing Affected Parts
-
Trim infected leaves or stems immediately.
-
Dispose of them properly; do not compost infected material.
Improve Air Circulation
-
Space plants properly to reduce humidity.
-
Prune crowded areas to allow better airflow.
Fungicidal Sprays
-
Use fungicides labeled for powdery mildew.
-
Apply according to instructions, usually every 7–14 days.
Organic Solutions
-
Neem oil: Effective as a preventive and treatment spray.
-
Baking soda mixture: Mix 1 tablespoon of baking soda with 1 gallon of water and a few drops of dish soap. Spray on affected areas.
Maintain Proper Garden Care
-
Avoid over-fertilizing with nitrogen, as it encourages fungal growth.
-
Water at the base of plants rather than overhead to reduce leaf wetness.
-
Mulch around plants to prevent soil-borne spores from spreading.
Prevention Tips for Powdery Mildew
-
Choose resistant plant varieties whenever possible.
-
Keep your garden clean and free of plant debris.
-
Rotate crops each season to avoid recurring fungal buildup.
-
Monitor plants regularly to catch infections early.
FAQs About Powdery Mildew
1. Can powdery mildew kill my plants?
While rarely fatal, powdery mildew can weaken plants, reduce growth, and lower fruit or flower yield if untreated.
2. Is powdery mildew contagious?
Yes, it spreads through spores carried by wind, insects, and contaminated tools. Early detection is key.
3. Can I eat vegetables with powdery mildew?
It’s best to avoid consuming infected parts. Remove and discard affected leaves or fruits.
4. How long does powdery mildew last?
With proper treatment, symptoms usually improve within 1–2 weeks. Persistent infections may require repeated powdery mildew treatment.
Click here to learn more
